Nasopharyngeal Airway (NPA)
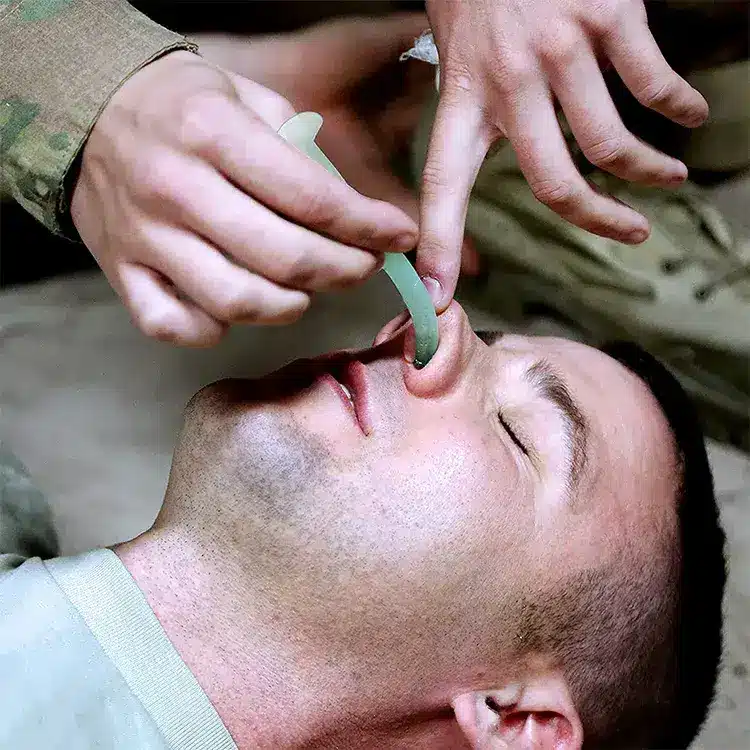
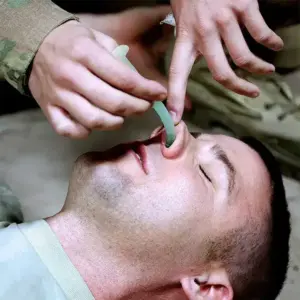
Nasopharyngeal Airway (NPA Airway) is a medical device designed to maintain the patency of a patient’s airway. It is typically made of flexible rubber or silicone and has a curved shape, with one end being narrower and the other end wider. The narrow end is inserted through the nostril and into the nasopharynx, helping to prevent airway obstruction and facilitating effective ventilation, especially in situations where the tongue may obstruct the oropharynx. NPAs are commonly used in emergency medicine, anesthesia, and critical care settings to ensure proper airflow and oxygenation in patients.
Features
Flexibility and Comfort: NPAs are made from soft, pliable materials such as rubber or silicone, providing flexibility and comfort during insertion, minimizing the risk of trauma to the nasal passages and airway structures.
Easy Insertion: The tapered design allows for relatively straightforward insertion through the nostril into the nasopharynx, making it a quick and efficient means of establishing and maintaining a patent airway.
Tolerance of Gag Reflex: Unlike oropharyngeal airways, NPAs are generally better tolerated by conscious patients because they do not stimulate the gag reflex, facilitating their use in individuals who are awake or semi-conscious.
Less Likely to Cause Vomiting: The presence of an NPA is less likely to induce a vomiting reflex compared to some other airway devices, reducing the risk of aspiration.
Facilitation of Oral Procedures: NPAs are especially useful in situations where oral access is restricted or when oral airways are contraindicated, such as in patients with maxillofacial injuries or those undergoing certain dental procedures.
Compatibility with Imaging: NPAs are often compatible with various imaging techniques, allowing medical professionals to monitor the placement and positioning of the airway device using X-rays or other imaging modalities.
Suitability for Head and Neck Trauma Patients: Due to their design, NPAs are appropriate for patients with head or facial trauma, as they can help secure a clear airway without exacerbating potential injuries.
Effective in Preventing Tongue Obstruction: NPAs are particularly effective in preventing airway obstruction by the tongue, which can occur in unconscious or sedated patients.
Versatility: Nasopharyngeal tube are available in various sizes, making them suitable for a wide range of patients, from pediatric to adult populations.
Emergency and Pre-hospital Use: NPAs are frequently employed in emergency medicine and pre-hospital settings, as they offer a rapid and reliable means of securing an airway in critical situations.